The Trend of Going Intelligent
The booth of AUBO Robotics, a Beijing-based company specializing in manufacturing robots, looked like a scene out of a sci-fi film. At last year’s Apsara Conference, an annual technology event held in Hangzhou in east China, two massage robots were presented. A woman lay face up on a makeshift bed, her shirt pulled up to expose her stomach. A white robot stood next to the bed, its long cylindrical arm moving gently over her midrib, which was glistening.
A company official explained it was emitting radio waves to gently heat up the body, following the Chinese medical principle that people fall ill when their bodies lose heat. Then, guided by the camera on its tip, the arm began tracing an arc on the body, massaging it expertly to give relief from inflammation and arthritic pain.
It is a development boosted by the COVID-19 pandemic. Since 2020, the market for COVID-19 control and prevention-related smart products has seen a boom. For example, an artificial intelligence system was launched by a Chinese research institute to analyze CT scan images in 20 seconds with 96 percent accuracy. Today, more than 600 hospitals in China are using the system. It is also employed by medical institutions in Europe and South America.
Another innovation is a mobile disinfection robot manufactured by Standard Robots, which can disinfect rooms as well as equipment, improving steralization in a complicated work environment.
While the global manufacturing industry faced difficulties such as workforce shortage and increasing costs, Chinese companies discovered opportunities in the crisis. A number of intelligent manufacturing companies have pioneered smart production lines with automatic workshops and smart factories. In this way, the “China speed” has remained unabated even during the pandemic.
However, the intelligent manufacturing industry in China is still far from reaching its full potential. It has a long way to go to transform from “Made in China” into “Intelligent Manufacturing in China,” and the pandemic presents a window of opportunity.
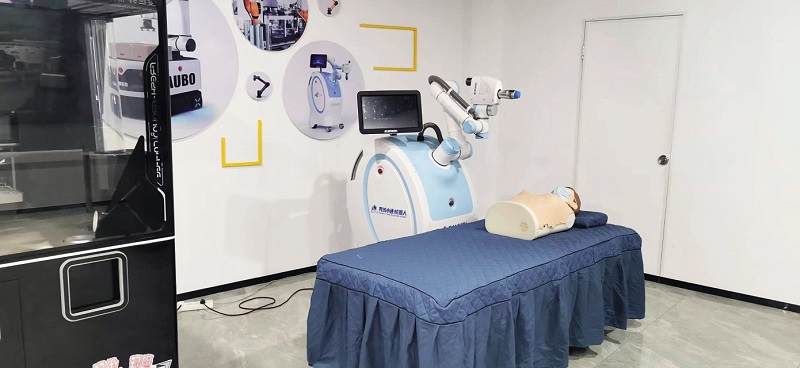
With the AUBO fractional wave massage robot, massage, diagnosis, file creation, and other tasks can be completed by only one person and one machine.
Business Opportunities
In addition to the COVID-19 control and prevention-related market, personnel shortages and factory shutdowns have made the manufacturing industry speed up production automation. This has brought huge opportunities for intelligent manufacturing companies.
Haier Smart Home, which manufactures intelligent home products like smart fridges that can identify family members using facial, voice, and image recognition, has a smart factory in Foshan in south China. The factory resumed work during the labor shortage and yet achieved a higher daily production than before by adopting intelligent production lines.
Another company AAC Technologies, which makes smart wearable devices, made significant investment to start over 70 automated production lines in its Changzhou base in east China. Only six people can now produce 10,000 speakers per day, which is a record in the industry.
Autonomous driving technology has been supporting medical supply distribution. Baidu Apollo started autonomous driving cloud services for quick dispatch of disinfection and delivery vehicles.

Standard composite mobile robot displayed at an exhibition.
Record Patent Drive
According to IncoPat Global Technology Analysis & Operation Platform, a patent database provider, the number of patent applications related with the pandemic has rocketed, 365 AI related patents have been applied, covering intelligent consultation, COVID-19 detection, intelligent monitoring during medical treatment and so on. In the first half of 2022, there were applications for 249 patents for automatic temperature measurement devices, of which 50 were authorized. Transportation is a critical sector and information service systems such as pandemic maps and tracking are required to trace suspected patients and their co-passengers. Baidu, State Grid and other companies have filed 138 patent applications in the area of transporting big data.
According to Chen Weiran, vice president of IncoPat, patent applications in AI, robotics, online medical consultation and other related fields have shown great momentum in the intelligent manufacturing sector. “We can be sure that intelligent manufacturing not only plays a key role in the fight against COVID-19, but will also become one of the major driving forces of economic growth after the pandemic,” Chen said.
Supported by national policies and increasing investment in digitalization, China’s intelligent manufacturing market has been expanding steadily. The market value for intelligent manufacturing is expected to rise to RMB 3.3 trillion (US $49.2 million) in 2022, compared to RMB 2.5 trillion (US $37.3 million) in 2020, growing approximately 30 percent in two years, according to Research Report on Market Prospects and Investment Opportunities of China’s Intelligent Manufacturing Industry published by ASKCI Research.
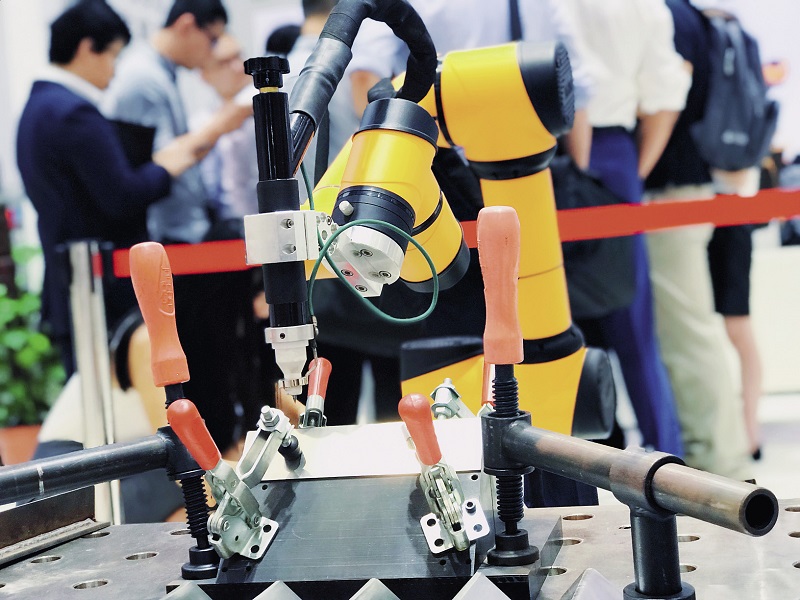

The AUBO argon arc welding robot adopts a light-weight work table, which is free from the traditional fixed and cumbersome welding mode, suitable for indoor and outdoor working environments.
Challenges Ahead
Despite the rapid growth, many challenges need to be tackled before the Chinese intelligent manufacturing players can catch up with the world leaders. First of all, although China has a huge market and the most diversified usage scenarios, Chinese companies have limited core technologies. Some key components such as precision motors and industrial cameras are mainly imported. More companies focus on application rather than on technology, which leads to a lower market share in the high-end segment. Besides, Chinese companies’ brand awareness and comprehensive competitiveness in the global market need to be improved.
Second, upgrading to intelligent manufacturing needs continuous investment. Since the “Made in China 2025” strategy was launched in 2015, intelligent manufacturing has become a hot sector in the primary market and investment has been growing, even during the pandemic. Nevertheless, China’s prevailing capital utilization rate remains low. Investments mainly go to transactions and circulation, with less engagement in technology and manufacturing.
The investment data in China’s intelligent manufacturing industry show it is still in its infancy with huge potential left to be tapped. A robust financial market will not only provide a platform for hi-tech companies to raise funds, but will also play a key role in the transformation, optimization and restructuring of traditional enterprises.
Finally, there is a big gap in the talent pool. According to Eng Hwa Yap, dean of the School of Intelligent Manufacturing Ecosystem and the School of Robotics at the Xi’an Jiaotong-Liverpool University in Taicang, east China, by 2025, intelligent manufacturing in China will need 9 million people. But it is estimated the industry now has only half this number. To bridge this gap, intelligent manufacturing talents will have to be trained, with a greater focus on specialization, systematization and intellectualization within service enterprises.
“As we plan towards a post-pandemic world, the development of talent to face the future of work must be at the forefront of our priorities. This is to enable the country to not just meet its demands locally, but also to ensure that China is best placed to compete in an increasingly networked and complex world,” Yap said.
Businesses and individuals have realized that things will not go back to the way they were before COVID-19. Companies understand that intelligent manufacturing is a viable solution for scaling up production and maintaining business continuity. Going intelligent has become the general direction of the world.
blog comments powered by